
More sensitive operating leverage is considered riskier since it implies that current profit margins are less secure moving into the future. Operating Leverage is a financial ratio that measures the lift or drag on earnings that are brought about by changes in volume, which impacts fixed costs. Many small businesses have this type of cost structure, and it is defined as the change in earnings for a given change in sales. Other company costs are variable costs that are only incurred when sales occur. This includes labor to assemble products and the cost of raw materials used to make products. Some companies earn less profit on each sale but can have a lower sales volume and still generate enough to cover fixed costs.
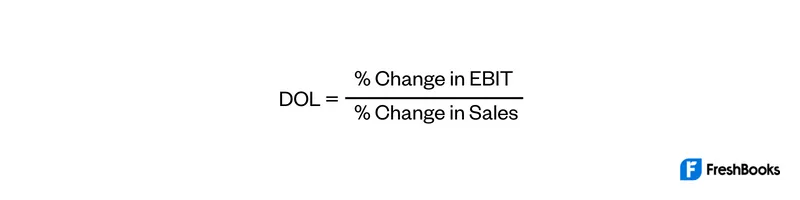
How to Calculate Earnings Per Share? (Definition, Using, Formula)
For example, for an operating leverage factor equal to 5, it means that if sales increase by 10%, EBIT will increase by 50%. By the way, if you find such a company, do not forget to contact us. The degree of operating leverage can never be harmful since it is a two-positive numbers ratio, i.e., sales and operating income. Moreover, the negative operating leverage implies that the operating income decreases as the revenue increases, which is inconsistent with the traditional definition of operating leverage. In contrast, a company with relatively low degrees of operating leverage has mild changes when sales revenue fluctuates.
Telecom Company Example
The higher the degree of operating leverage (DOL), the more sensitive a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are to changes in sales, assuming all other variables remain constant. The DOL ratio helps analysts determine what the impact of any change in sales will be on the company’s earnings. The impact of the high fixed costs is directly seen in the firm’s ability to manage revenue fluctuations. Regardless of the sales level, the fixed expenses have to be fulfilled. The high operating leverage reflects the inflexibility in managing costs and revenues.
How is Operating Leverage Used in Business?
Understanding the degree of operating leverage and its impact on the company’s financial health. The cost structure directly impacts all the other measures, including profitability, response to fluctuations, and future growth. For example, if your DOL was 1.25% in 2021 but dropped to .95% in 2022, it would mean your profit has decreased.
Final Thoughts: Operating Leverage Can Help You Predict Changes in Profit
While this information is available for those that wish to calculate their DOL internally, if you’re interested in calculating it for a competitor (which, by the way, you can do!), you’ll likely use the second formula. It does this by measuring how sensitive a company is to operating income sales changes. Higher measures of leverage mean that a company’s operating income is more sensitive to sales changes. Financial leverage is a measure of how much a company has borrowed in relation to its equity.
Increasing utilization infers increased production and sales; thus, variable costs should rise. If fixed costs remain the same, a firm will have high operating leverage while operating at a higher capacity. Essentially, operating leverage boils down to an analysis of fixed costs and variable costs. Operating leverage is highest in companies that have a high proportion belleville coyote one xero c320 ultra light assault boot of fixed operating costs in relation to variable operating costs. Conversely, operating leverage is lowest in companies that have a low proportion of fixed operating costs in relation to variable operating costs. Companies with high fixed costs tend to have high operating leverage, such as those with a great deal of research & development and marketing.
When variable costs are relatively high, degree of operating leverage is low and change in sales results in slower increase in operating income. Operating leverage measures a company’s fixed costs as a percentage of its total costs. It is used to evaluate a business’ breakeven point—which is where sales are high enough to pay for all costs, and the profit is zero.
- Regardless of the sales level, the fixed expenses have to be fulfilled.
- By the way, if you find such a company, do not forget to contact us.
- Financial and operating leverage are two of the most critical leverages for a business.
- In other words, the numerical value of this ratio shows how susceptible the company’s earnings before interest and taxes are to its sales.
- If sales and customer demand turned out lower than anticipated, a high DOL company could end up in financial ruin over the long run.
Whether it sells one copy or 10 million copies of its latest Windows software, Microsoft’s costs remain basically unchanged. So, once the company has sold enough copies to cover its fixed costs, every additional dollar of sales revenue drops into the bottom line. In other words, Microsoft possesses remarkably high operating leverage.
High operating leverage during a downturn can be an Achilles heel, putting pressure on profit margins and making a contraction in earnings unavoidable. Indeed, companies such as Inktomi, with high operating leverage, typically have larger volatility in their operating earnings and share prices. Return on equity, free cash flow (FCF) and price-to-earnings ratios are a few of the common methods used for gauging a company’s well-being and risk level for investors. One measure that doesn’t get enough attention, though, is operating leverage, which captures the relationship between a company’s fixed and variable costs.
